When mentioning gabions, it’s generally understood that they are cages designed in cubic or rectangular shapes, with six sides and filled with rocks inside. But why are gabions used? What are gabions? What is the structure of gabion mesh? How are gabions shaped? Let’s explore more accurate information about gabions with Phú Thành Phát through the article shared below!
What are Gabions?
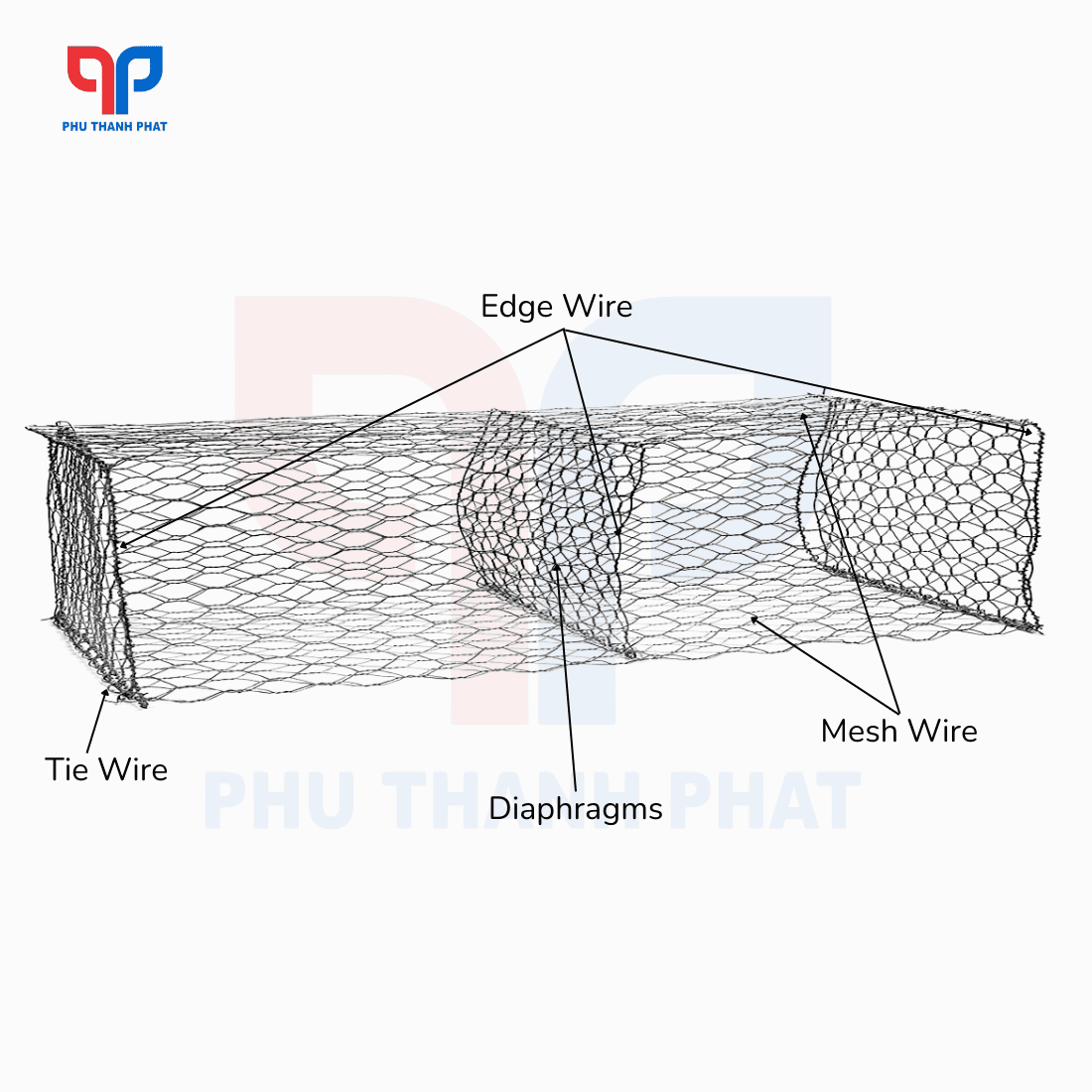
Gabions are a steel wire mesh system made from galvanized steel or PVC-coated galvanized steel wire cores, woven together into double-twisted hexagonal mesh and shaped using frame wires with a larger diameter to form a hollow geometric block for holding rocks. Each gabion has a lid (integral or separate, depending on size) and tie wires.

Gabion Structure
Gabions typically consist of three main parts:
- Mesh Wire: Made of stainless steel, with uniform quality and tensile strength. Twisted 2 or 3 times for strength. Available in two types: galvanized steel wire and PVC-coated galvanized steel wire.
- Edge Wire: Steel wire with a larger core diameter than the mesh wire. Used to secure the mesh panels and form a robust gabion frame.
- Tie Wire: Used to fasten and reinforce gabions together. Has the same characteristics and dimensions as the mesh wire. Used to connect the gabion lid to the cage.
- Diaphragms: Created from interconnected mesh wires.
Functions of Gabions
- Protection: Gabions have a steel wire structure with high deformation capacity, allowing them to withstand pressure from soil and water better. In cases where structures are built on weak geological areas, prone to erosion and landslides due to underground waves or strong flow pressure, the deformation function helps gabions remain stable, protecting the structure from structural and quality impacts.
- Load Bearing: Gabions are shaped by stacking layers and connecting them with tie wires to form a solid block. The rocks inside are tightly bound by the frame wires, preventing movement. This creates a strong interlocking force, enabling gabions to withstand external forces from the natural environment, increasing load-bearing capacity and structural lifespan.
- Erosion Control: One of the most critical functions of gabions is erosion control. This makes them indispensable in hydraulic and road construction. Over time, the interlocking of rocks in gabions is enhanced by the growth of plant roots, weeds, moss, or sediment filling the voids, improving erosion resistance and maximizing their effectiveness.
- Drainage: Gabion mesh forms permeable openings, allowing for rapid water drainage. This is widely applied in projects in flood-prone areas or in building drainage embankments. To maximize drainage, use standard gabions with small rocks to create optimal porosity. For example, use gabions with small mesh sizes like 60x80mm to contain small rocks, ensuring good drainage and ease of installation.
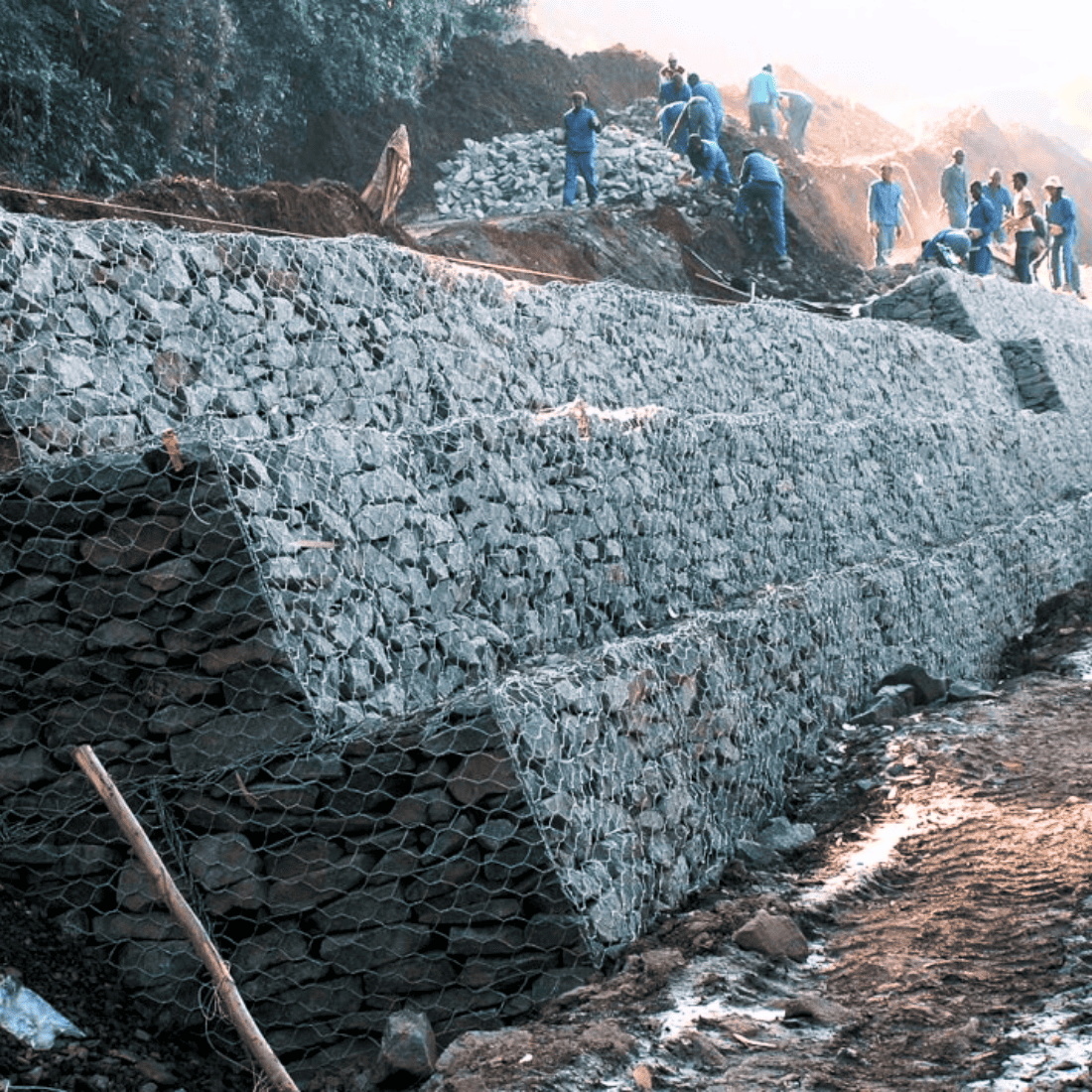
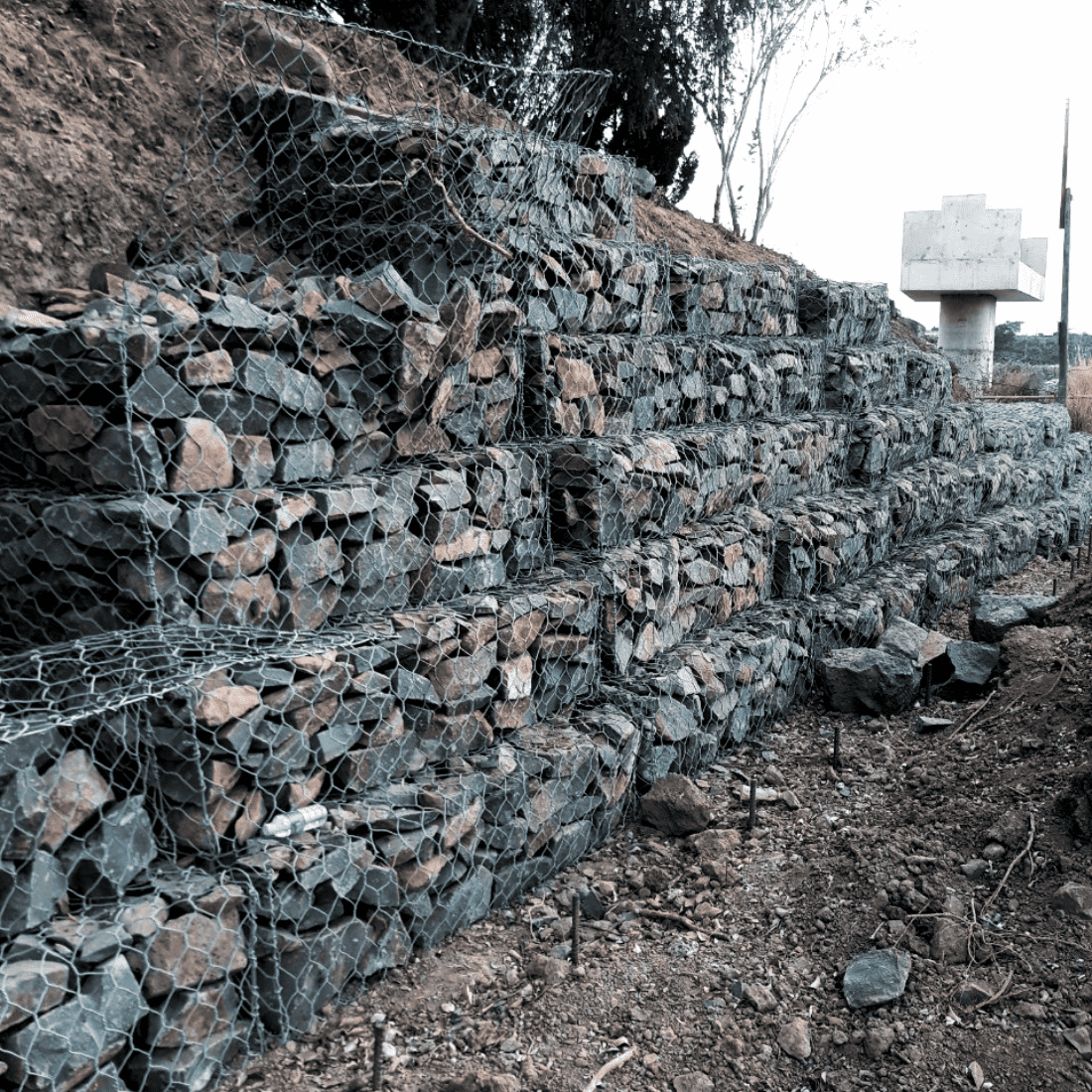


Applications of Gabions
Gabions are used in applications requiring load bearing, structural reinforcement, drainage, and erosion control, such as:
- Retaining walls, gravity walls, or water retaining walls like seawalls and riverbanks to regulate underground currents.
- Foundation structures, footings, bridge piers, etc.
- Slope protection, channel lining, ditch lining, etc.
- Gravity dam structures, flow control, water barriers, etc.
Common Types of Gabions
Gabions come in various types and sizes, classified based on two main criteria:
- Based on Gabion Structure: Two main types: galvanized gabions and PVC-coated galvanized gabions.
- Based on Gabion Shape: Six types: gabions, rock mattresses, gabion mattresses, rock cylinders, anchored gabions, and rock boxes.
Let’s explore these classifications in more detail below.
Classification Based on Gabion Structure
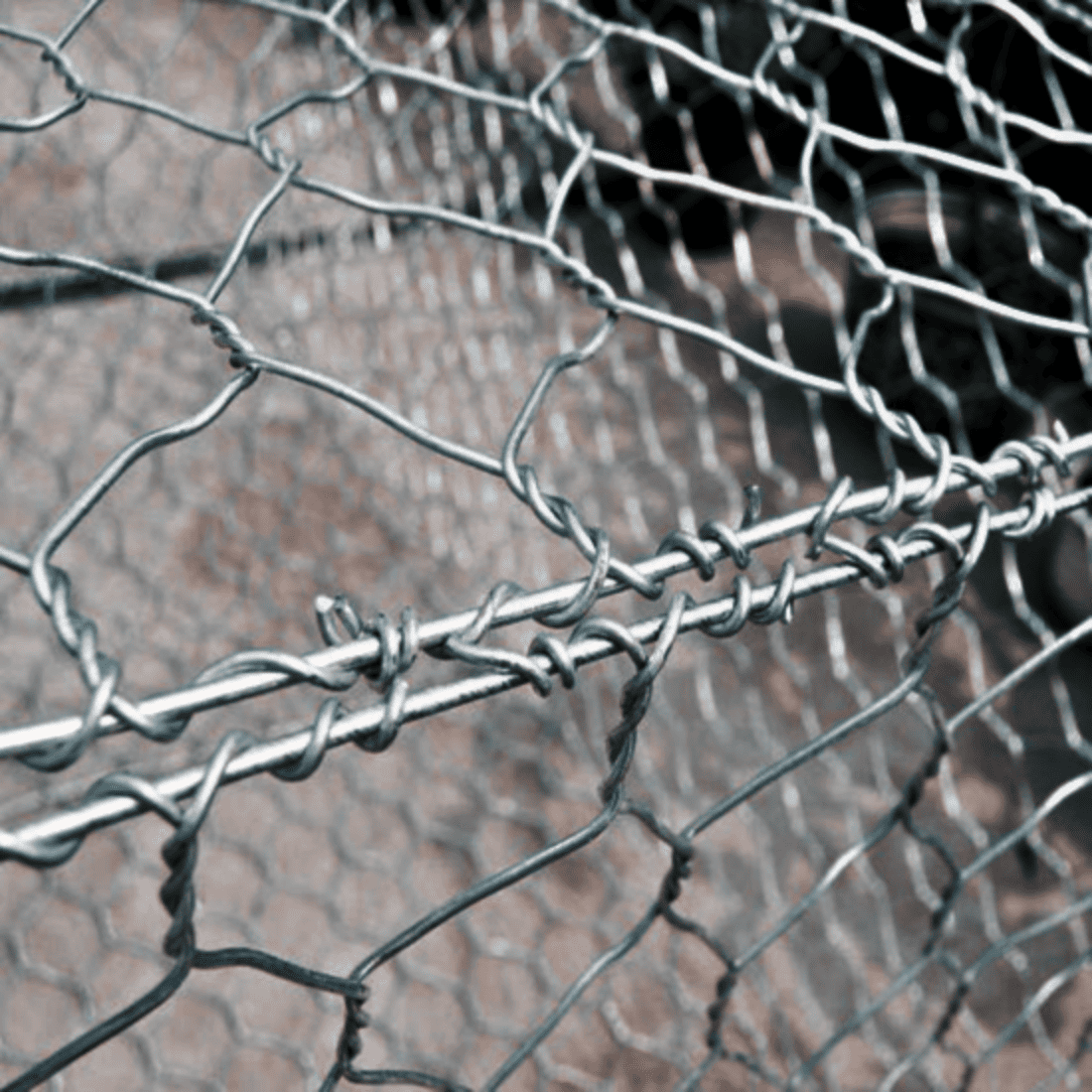

Galvanized Gabions
These are made from hot-dip galvanized steel wires woven into mesh. They are typically used in onshore projects or areas with minimal oxidation, such as landslide prevention on mountain passes and slope stabilization at mountain bases.

PVC-Coated Galvanized Gabions
These are made from hot-dip galvanized steel wires coated with PVC. This coating provides higher oxidation resistance than galvanized gabions, making them suitable for highly corrosive environments like hydraulic projects such as riverbanks, seawalls, streams, canals, ditches, and hydraulic dams.
Classification Based on Gabion Shape
- Gabions: The most common type, rectangular boxes with or without partitions, used to contain rocks and connected with tie wires. Internal partitions are used in longer gabions to prevent rock movement. Primarily used for protection, reinforcement, and load bearing in applications like gravity retaining walls, footings, and reinforced earth walls.
- Rock Mattresses: Similar to gabions but with different dimensions, height < 0.5m and length > 3m. Internal partitions are 1m long to prevent rock displacement, enhancing interlocking and load-bearing capacity. Mainly used for erosion control, protecting embankment toes, and lining riverbanks and seawalls.
- Gabion Mattresses: A combination of gabions and rock mattresses, height >= 0.5m, rectangular boxes with 1m partitions. Used when both erosion control and load-bearing capacity are required, in applications like:
- Marine structures (breakwaters, harbor protection, etc.).
- Projects with high flow velocities and complex hydrological conditions.
- Super heavy-duty embankment protection.
- Rock Cylinders (Rock Sausages): Unlike gabions and rock mattresses, these are cylindrical gabions formed by connecting steel mesh edges and tying the ends after filling with rocks. Used in hydroelectric dams, temporary ports, and underground erosion control in uneven terrain.
- Anchored Gabions: Special gabions with an L-shape, including a gabion and a steel anchor mesh fixed to it. The gabion provides structural support and protects reinforced soil from external forces like settlement and erosion, while the anchor mesh provides reinforcement. Mainly used for erosion control on riverbanks with strong currents and in special structures like breakwaters and embankment toes.
- Rock Boxes: Standard gabions filled with large rocks or boulders. Due to the large rock size, the mesh size is also larger (approximately 14cm-20cm). Standard dimensions are 2mx1mx0.5m (length/width/height). Rock boxes have high load-bearing capacity and are mainly used for retaining walls and landscape walls.
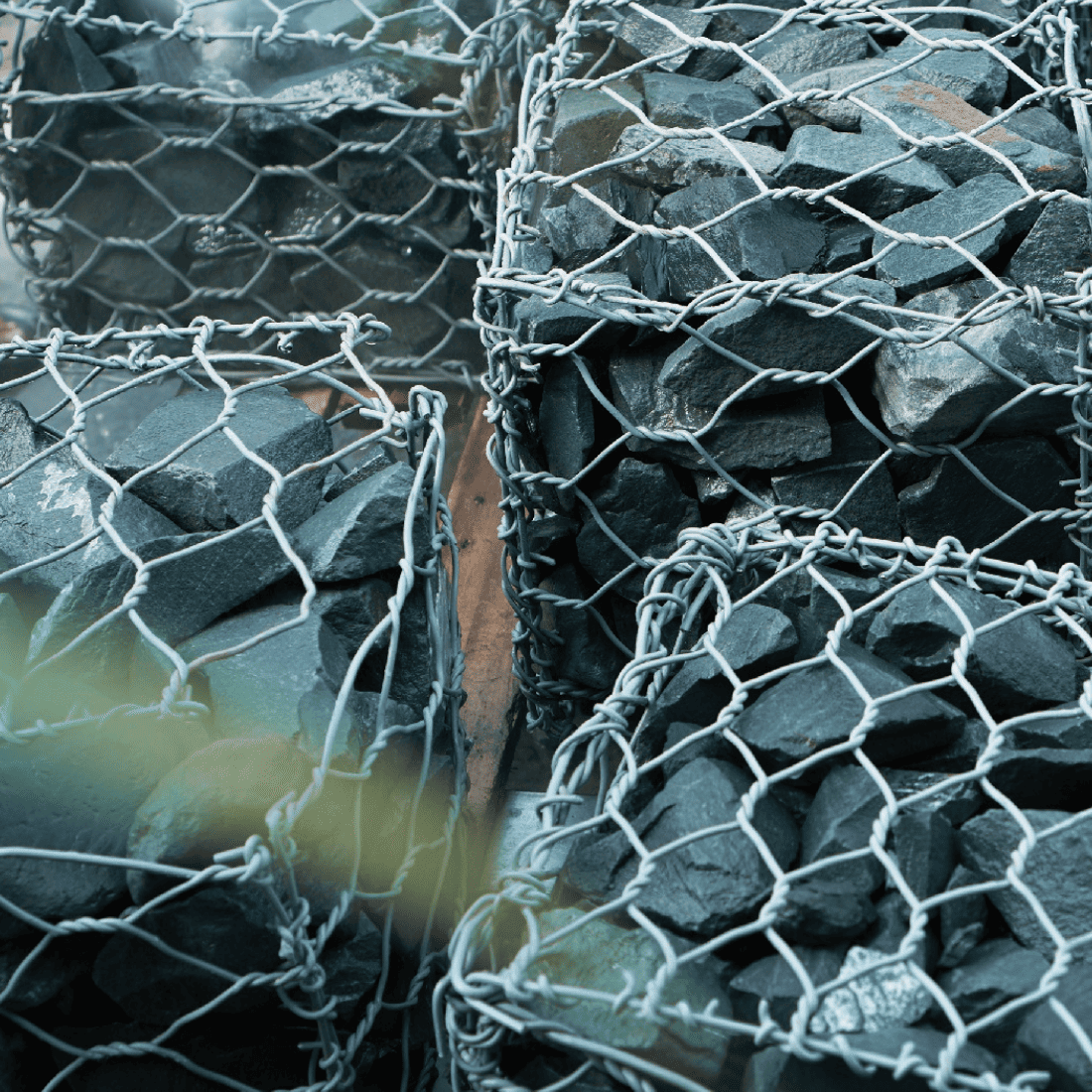

Common Gabion Sizes
Gabions come in various sizes to suit different needs. Common sizes include 60x80mm, 80x100mm, and 100x120mm with double-twisted wire mesh. Special gabions can have mesh sizes up to 200mm. Common dimensions include:
- Mesh wire diameter: 2-3mm
- Edge wire diameter: 2.7-6mm
- Common mesh size: 8x10mm, 10x12mm, 12x14mm, 14x16mm
- Standard gabion dimensions: 2x1x0.5mm with P10 mesh (10x12mm), 2.7mm mesh wire, 3.4mm edge wire.
Phú Thành Phát is the first to research and produce triple-twisted hexagonal mesh gabions. These gabions have high wire tension, improving performance compared to standard double-twisted mesh.
Conclusion
Gabions have four main functions: protection, load bearing, erosion control, and drainage. They are classified based on structure and shape, with each type having different sizes and applications. For inquiries or quotes, please leave your contact information or contact Phú Thành Phát directly. We will provide prompt assistance and quotes.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Head Office: 15 Street 5, Vinh Loc Residential Area, Binh Hung Hoa B Ward, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
Hotline: 028.666.03482 – 0909.452.039 – 0903.877.809
Email: info@vaidiakythuat.com
